 |
1950
President Truman announces that the United States will accelerate the atomic energy program.
1950
Curtis Nelson, Atomic Energy Commission (AEC), and Robert K. Mason, DuPont, are selected as managers for a yet-to-be-determined plutonium and tritium production plant.
1950
President Truman sends a formal letter to DuPont, specifically requesting their expertise for the new project.
|
1950
Selection of location of Savannah River Plant (SRP), between Aiken, S.C., and Augusta, Ga., on the Savannah River, is announced.
1951
Site construction begins.
1951
Environmental monitoring of SRP begins with Dr. Ruth Patrick's baseline survey.
1951
Construction completed on CMX pilot plant, the first working facility at SRP.
|
1951
First waste tank construction begins.
1952
Heavy water production starts in D Area.
1952
305-M graphite test pile is the first reactor to go critical at SRS.
|
1953
R Reactor startup
1954
P, L, K Reactors and F Canyon startup
1954
F Area is the first separations plant to begin operation.
1954
First shipment of plutonium to the Atomic Energy Commission
|
1955
Permanent Tritium facilities operational
1955
C Reactor and H Canyon startup
1955
First shipment of tritium to the AEC
1956
Neutrino confirmed at P Reactor
1957
Heavy water facilities reduced and reworked due to an adequate supply of heavy water for operations and sale
|
1958
Par Pond provides cooling water for P and R Reactors
1959
First production of Pu-238 heat source. SRP plutonium would first be used in a space satellite launched December 30, 1961.
1959
F Area restarted after two years of upgrades and addition of
FB Line
 House being relocated from the future Savannah River Plant
House being relocated from the future Savannah River Plant SRP offered employment to thousands
SRP offered employment to thousands Reactor startup
Reactor startup One-piece plastic suit designed
One-piece plastic suit designed 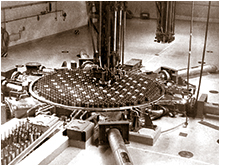 Closeup of plenum while reactor's charge and
Closeup of plenum while reactor's charge and